Project: “Decoding Human Behavior from Brain Electrical Signals (Deep Brain Stimulation/Parkinson’s disease)”
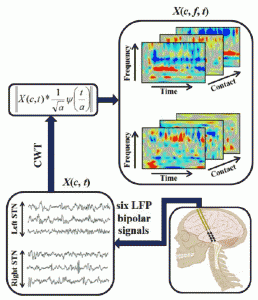 This project focuses on developing a robust pattern recognition system to recognize and classify human’s behavior (e.g. language and motor tasks) from different brain electrical signals. The objective of this project is to advance research concerning next generation of closed-loop deep brain stimulation (DBS) systems, which are widely used to treat movement disorders such as Parkinson’s disease (PD). This project explores a unique data set of simultaneous recordings of cortical and subcortical electrical potentials in the human brain (e.g., local field potential) obtained during surgical implantation of a DBS system.
This project focuses on developing a robust pattern recognition system to recognize and classify human’s behavior (e.g. language and motor tasks) from different brain electrical signals. The objective of this project is to advance research concerning next generation of closed-loop deep brain stimulation (DBS) systems, which are widely used to treat movement disorders such as Parkinson’s disease (PD). This project explores a unique data set of simultaneous recordings of cortical and subcortical electrical potentials in the human brain (e.g., local field potential) obtained during surgical implantation of a DBS system.
PD is a neurodegenerative condition and movement disorder diagnosed on the basis of clinical history and motor signs of tremor, rigidity and bradykinesia. PD incidence increases with advancing age and peaks among people in their 60s and 70s. DBS is an advanced FDA-approved therapeutic technique for alleviating the PD symptoms especially for whom drug therapy is no longer efficient. DBS of the subthalamic nucleus (STN-DBS) improves motor signs of PD and permits reduction of dopaminergic medication. Existing DBS therapy is open-loop, providing a time invariant stimulation pulse train that is not customized to a patient’s current behavioral task goals. By customizing DBS therapy to a patient’s task using machine learning and signal processing methods, these side effects of stimulation may arise only when they are non-detrimental to the patient’s current goals. This could therefore allow more aggressive DBS parameters (e.g. closed-loop DBS) to be used with a reduced risk for therapy limiting side effects.
Recent Related Publications:
- H. M. Golshan, A. O. Hebb, S. J. Hanrahan, J. Nedrud, and M. H. Mahoor, “An FFT-based synchronization approach to recognize human behaviors using STN-LFP signal,” ICASSP, 42nd IEEE International Conference on., pp. 979-983, Mar. 2017.
- H. M. Golshan, A. O. Hebb, S. J. Hanrahan, J. Nedrud, and M. H. Mahoor, “A multiple kernel learning approach for human behavioral task classification using STN-LFP signal,” EMBC, 38th IEEE International Conference on., pp.1030-1033 2016.
- A.O. Hebb, H.M. Golshan, S.J. Hanrahan, J. Nedrud, M.H. Mahoor, “Behavior Classification using Multi-site LFP and ECoG Signals”, Society for Neuroscience, San Diego, CA, USA, Nov. 2016.
- S. Niketeghad, A. O. Hebb, J. Nedrud, S. J. Hanrahan, and M. H. Mahoor, “Motor task event detection using subthalamic nucleus local field potentials,” EMBC, 37th IEEE International Conference on., pp. 5553–5556, 2015.
- S. Niketeghad, A. O. Hebb, J. Nedrud, S. J. Hanrahan, and M. H. Mahoor, “Single trial behavioral task classification using subthalamic nucleus local field potential signals,” EMBC, 36th IEEE International Conference on., pp. 3793–3796, 2014.
